LiFi uses LED lights to transmit data (pureLiFi)
There are many things people take for granted in life: clean water, food, public transportation, sunlight, free Wi-Fi.
OK, scratch the last one. However, the possibility of internet access for everyone could become reality. That light bulb over your head (literally) can transmit signals -much in the same way Wi-Fi does- that hook your computer up to the internet. Already some grocery stores in France are using Li-Fi to track consumer’s shopping habits. While the light fidelity technology is still in its early phases, it’s shown tremendous potential. The global market is projected to expand to $115 billion by 2022 and could conceivably replace Wi-Fi.
Here’s what you need to know about the nascent, but promising technology.
1. Li-Fi Harnesses the Power of Visible Light Instead of Radio Waves Used by Wi-Fi
Although you can’t see them, waves are transmitted from our devices, carrying bits of data that allow us to surf the Internet. They communicate with towers called cellular radio masts, which you might see disguised as palm trees. There are approximately 1.4 million cellular radio masts worldwide, according to the founder of LiFi, Harald Haas.
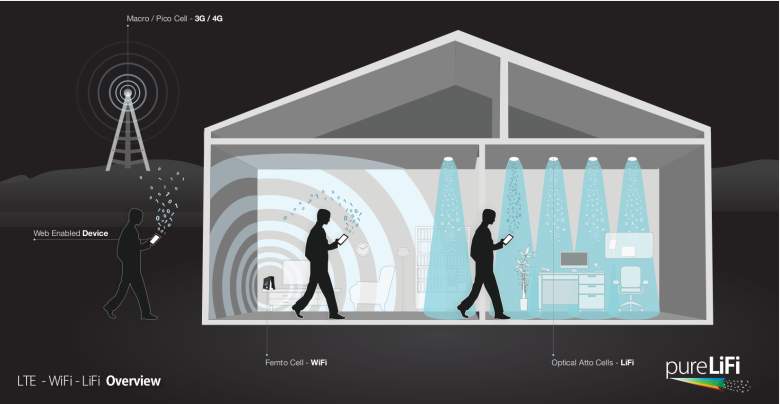
Li-Fi replaces this bulky infrastructure, with a elegant, illuminating solution. It depends on LED lights that send data over visible light via pulses that the human eye can’t detect. On the electromagnetic spectrum, which measures the frequency of radiation, the spectrum of visible light is 10,000 times as big as that of radio-waves says Haas. Using light could eliminate the expenses resulting from the limited range of radio waves.
“[Light] has created us, has created life, has created all the stuff of life. So it’s inherently safe to use. And wouldn’t it be great to use that for wireless communications?” said Haas in a 2011 Ted Talk.
2. Li-Fi Has Been Integrated into Some Smartphone Cameras

Future iPhones may use light to connect to the Internet
Li-Fi not only requires LED light bulbs to transmit data, but also a receiver that can interpret that data. In January it was reported that Apple had referenced Li-Fi capabilities in versions of the iPhone, iOS 9.1 and up. Visible light communication has also been used in a grocery store in Northern France to track the location of customers with their consent. This provides invaluable data to marketers, who can offer coupons and other incentives based on shopping habits.
However, Li-Fi has much bigger applications than simply as a geo-location tool. Incorporating LiFi into the 14 billion existing light bulbs could provide more accessible and secure internet service, says Haas. Haas has proposed retrofitting the existing Internet framework to support Li-Fi bulbs. To that end, he created the company pureLiFi, which provides internet at speeds of first generation WiFi.
3. The Inventor of LiFi started a Company Called pureLiFi and Microsoft is a Fan

pureLiFi’s first product: Li-1st (pureLiFi)
The professor of mobile communications at the University of Edinburgh, Haas founded pureLiFi in 2012 after introducing the world to the technology in a 2011 Ted Talk. Haas thought his personal LiFi project could revolutionize Internet access. Since it was founded, pureLiFi came out with its first product Li-1st in 2013. The LiFi pioneer consisted of an ethernet-connected LED light and a desktop receiver. Its third generation device improves on device speed with 40 mbps uplink and downlink. However, the beauty of LiFi is not in its speed, but its accessibility. Several LiFi light bulbs can be placed in room that can only support one WiFi router, according to Haas’s website. That means there’s enough bandwidth for everyone!
pureLiFi has partnered with LED light maker Lucibel to develop the technology. The France-based company heralded the applications of LiFi for the Internet of Things, a network of devices that communicate with each other. Their first industrialized LiFi product, the LiFi luminaire, launched in September. Real estate development company Nexity was the first end user of the LiFi technology. Microsoft will also be using the technology at its innovation center in Issy-les-Moulineaux.
4. LiFi is Virtually Hack-Proof
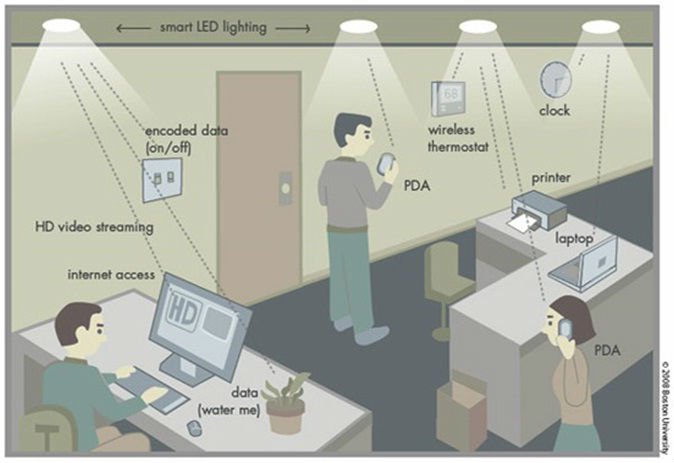
LiFi stops criminals from peeping in on your Internet connection (Boston University)
Because light can’t penetrate through walls, it’s very difficult to tap sensitive data transmitted through LiFi. It’s not uncommon for criminals to steal personal information from unsuspecting Internet users at a local cafe. Even password protected WiFi can be hacked, allowing criminals to see what web pages you visit and links you click on. That said, LiFi offers a more secure alternative to WiFi because available data can be confined to a room.
Of course, there’s a trade-off between convenience and security. However, smart architecture would allow light to follow a user, according to Forbes. Scientists are also working on technology to make Li-Fi work in the dark. Dartmouth University researchers discovered that dim LEDs would be able to send pulses undetectable by the human eye.
LiFi can be Applied in Settings Where WiFi Doesn’t Work
Where there’s a LED light bulb, there’s a potential application for LiFi. In his Ted Talk, Haas rattled off Li-Fi applications from in-flight internet access to a traffic control system using car’s headlights. He also stressed the applications for high security places that can’t use radio frequency. For example, he said radio frequency could cause antenna sparks at a petrochemical plant. In a reference to Internet-connected devices, he proposed using Li-Fi in hospital settings to power medical instruments.
Comments
LiFi Technology: 5 Fast Facts You Need to Know